![]()
![]()
![]()
ชื่อส่วนงาน : สถาบันแห่งชาติเพื่อการพัฒนาเด็กและครอบครัว (National Institute for Child and Family Development)
ชื่อเรื่อง : โครงการวิจัยเพื่อติดตามผลกระทบจากสารอาร์เซนิก แมงกานีส ไซยาไนด์ และฟื้นฟูภาวะบกพร่องทางสติปัญญา
กระบวนการรู้คิด และการเรียนรู้ในเด็กประถมศึกษาปีที่ 4-6 (Research Project for Follow up the Effect of Arsenic,
Manganese, Cyanide and Promotion of Cognitive and Learning Disability in Elementary School Grade 4-6)
นักวิจัย : หัวหน้าโครงการวิจัย ดร.นุชนาฎ รักษี (Dr.Nootchanart Ruksee), รศ.อดิศักดิ์ ผลิตผลการพิมพ์
และคณะวิจัยของสถาบันแห่งชาตเพื่อการพัฒนาเด็กและครอบครัว และหน่วยงานภาครัฐ ชุมชนและโรงเรียนในพื้นที่

 |
| รองศาสตราจารย์ นายแพทย์อดิศักดิ์ ผลิตผลการพิมพ์ |
 |
| อาจารย์ ดร.นุชนาฏ รักษี |
ชื่อวารสารตีพิมพ์เผยแพร่งานวิจัย : ข้อเสนอแนะเชิงนโยบายจากโครงการวิจัย (Policy Recommendations from Research)
สรุปผลวิจัย : ยุทธศาสตร์การศึกษาของชาติเน้นการพัฒนาศักยภาพเด็กไทยทุกคนให้มีทักษะในศตวรรษ ที่ 21 หมายรวมถึงเด็กในพื้นที่เสี่ยงผลกระทบจากอุตสาหกรรมโลหะหนัก จากการศึกษาในปี พ.ศ. 2559 พบมีอุบัติการณ์การรับสัมผัสสารหนูอนินทรีย์ในปัสสาวะในเด็ก ร้อยละ 36.1 ซึ่งโลหะหนักเช่น สารหนู เป็นสารพิษที่มีฤทธิ์ต่อความผิดปกติทางสติปัญญา จึงนำมาสู่วัตถุประสงค์ของการศึกษาครั้งนี้ เพื่อติดตามสถานการณ์ภาวะบกพร่องทางสติปัญญา กระบวนการรู้คิด และการเรียนรู้ของเด็ก เพื่อนำไปสู่การฟื้นฟูภาวะบกพร่องทางสติปัญญาและการเรียนรู้ของเด็กโดยการมีส่วนร่วมของครู รวมทั้งให้เด็กตระหนักและมีความรู้ในการป้องกันตนเองจากสารพิษ ในชั้นประถมศึกษาปีที่ 4-6 ใน 6 โรงเรียนเดิมที่ตั้งอยู่ในพื้นที่เสี่ยงอุตสาหกรรมโลหะหนัก
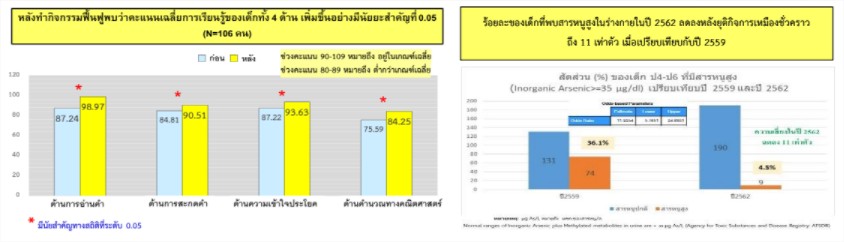
ผลการวิจัยพบว่า ลักษณะของครอบครัวที่เด็กอาศัยอยู่ด้วยเป็นครอบครัวแหว่งกลาง ที่พ่อแม่เด็กไม่ได้อาศัยอยู่กับเด็กในหมู่บ้านเนื่องจากไปทำงานนอกหมู่บ้านถึง ร้อยละ 82.60 เด็กได้รับการเลี้ยงดูจากปู่ย่าตายายถึง ร้อยละ 38.70 ส่วนการตรวจปริมาณสารโลหะหนักในร่างกายเด็ก พบว่ามีอุบัติการณ์การรับสัมผัสสารหนูอนินทรีย์ในปัสสาวะมากกว่าเกณฑ์ปกติ ร้อยละ 4.5 ซึ่งลดลงเกือบ 11 เท่าตัว จากการประเมินทักษะสติปํญญาและการเรียนรู้ของเด็กทั้งหมดจำนวน 212 คน พบว่า เด็กมีความบกพร่องทางการเรียน ใน 4 ด้าน ได้แก่ การอ่านคำ ด้านการสะกดคำ ด้านความเข้าใจประโยค ด้านการคำนวณทางคณิตศาสตร์โดยมีปัญหาการเรียนรู้ ตั้งแต่ 1 ด้านขึ้นไปถึงร้อยละ 81.60 และในกลุ่มเด็กที่มีระดับสติปัญญา (IQ) ปกติ (IQ≥ 90) จำนวน 126 คน นั้นพบว่า เด็กมีภาวะบกพร่องทางการเรียนรู้ ร้อยละ 22.22 ส่วนการสำรวจในปี พ.ศ. 2559 พบภาวะบกพร่องทางการเรียนอยู่ที่ ร้อยละ 38.9 ซึ่งสูงกว่าปี 2562 ผลหลังการฟื้นฟูเด็กที่มีความบกพร่องทางการเรียนโดยเมื่อเปรียบเทียบผลก่อนและหลังการฟื้นฟู พบว่า เด็กที่ได้รับการฟื้นฟู มีทักษะการอ่านคำ สะกดคำ ความเข้าใจประโยค ด้านการคำนวณทางคณิตศาสตร์เพิ่มขึ้นอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ หลังฟื้นฟูพบว่า เด็กมีคะแนนเฉลี่ยของระดับสติปัญญา เท่ากับ 90.11 เมื่อวิเคราะห์เปรียบเทียบความแตกต่าง พบว่า เด็กมีคะแนนเฉลี่ยระดับสติปัญญาหลังการฟื้นฟูสูงขึ้นแตกต่างอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ จากการสอบถามเด็กด้านความรู้ในการป้องกันตนเองจากสารพิษในสิ่งแวดล้อม พบว่าเด็กส่วนใหญ่ร้อยละ 64.2 มีระดับความรู้ในการป้องกันตนเองจากสารพิษอาร์เซนิก แมงกานีส และไซยาไนด์ อยู่ในระดับน้อย หลังการเข้าร่วมกิจกรรมส่งเสริมทักษะการรู้เท่าทันสิ่งแวดล้อม พบว่า กลุ่มตัวอย่างเด็กนักเรียนส่วนใหญ่ร้อยละ 41.9 มีระดับความรู้ในการป้องกันตนเองจากสารพิษเพิ่มขึ้น อยู่ในระดับปานกลาง และหลังฟื้นฟูมีความแตกต่างกันอย่างมีนัยสำคัญ นอกจากนั้นโครงการยังได้เผยแพร่งานวิจัยและขยายผลแก่สังคมในวงกว้าง โดยได้มีการจัดเวทีแถลงข่าวผลการวิจัย และจัดเวทีคืนข้อมูลในพื้นที่ เพื่อนำเสนอข้อมูลสำคัญจากการติดตามภาวะบกพร่องทางสติปัญญาและการเรียนรู้ รวมทั้งประเมินประสิทธิผลการส่งเสริมการเรียนรู้ และปัจจัยต่างๆ ที่ส่งผลกระทบต่อเด็ก ซึ่งในเวทีมีการระดมความคิดเห็นจากผู้แทนครูและผู้ปกครองจากโรงเรียนในพื้นที่ ผู้นำชุมชน องค์การบริหารส่วนตำบล ภาคการศึกษาจังหวัด ศูนย์การศึกษาพิเศษจังหวัด โรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบล และอาสาสมัครสาธารณสุขประจำหมู่บ้านในพื้นที่ เพื่อกำหนดทิศทางการจัดกิจกรรมฟื้นฟูพัฒนาการเรียนรู้ของเด็กอย่างต่อเนื่องในพื้นที่ นับเป็นการต่อยอดผลวิจัยสู่การใช้ประโยชน์บนการมีส่วนร่วมของทุกภาคส่วน นอกจากนั้นได้ส่งสรุปผลงานวิจัยเบื้องต้นแก่ 15 หน่วยงานภาครัฐ รวมทั้งภาคสังคมที่เกี่ยวข้อง และสารคดีสั้นเผยแพร่ทางสื่อออนไลน์ เพื่อนำใช้ขับเคลื่อนงานระดับนโยบาย และสังคม อันจะนำไปสู่การติดตาม ป้องกัน แก้ไขปัญหาและฟื้นฟูทักษะสติปัญญา การเรียนรู้ในเด็กได้ทันท่วงที และให้เด็กตระหนัก มีความรู้เท่าทันในการป้องกัน ดูแลตนเองอันจะเป็นการแก้ไขปัญหาอย่างยั่งยืนต่อไป โดยโครงการนี้ได้รับทุนสนับสนุนจาก สถาบันวิจัยระบบสาธารณสุข (สวรส.)
Thailand’s education strategy focuses on developing all Thai children to have skills in the 21st century, including children in areas at risk due to the effects of heavy metal industries. A study in 2016 found the incidence of non-organic arsenic in children’s urine to be 36.1%. Heavy metals such as arsenic are toxic substances with effects causing intellectual impairment, which led to the objective of this study to monitor the situation of intellectual, cognitive and learning impairments among children in order to lead to rehabilitation of children’s intellectual and learning impairments with teacher participation in addition to raising awareness and knowledge about self-protection from toxins among children in Grade 4-6 from 6 schools which were originally located in risk areas with heavy metal industries.
The findings revealed the children’s family characteristics to be medium-sized families with parents not living with children in the village because the parents worked outside the village (82.60%). Most of the children were raised by grandparents (38.70%) and most of the parents had primary education levels. The families were in poverty with a mean monthly income of 5,000 – 10,000 baht (49.60%). From health examinations of 199 children, the incidence of contact with non-organic arsenic in the urine was found to be higher than usual (4.5%), a reduction by nearly 11 times in boys and girls of every class and school when compared to a previous survey in 2016. According to assessment of cognitive and learning skills in 212 students, students were found to have learning impairments in 4 areas, namely reading, spelling, sentence comprehension and mathematic calculations. The sample had learning impairments in one or more areas (81.60%). Survey results in 2016 found learning impairments at a rate of 38.9%, which was higher than in 2019. When the results following rehabilitation among children with learning impairments were compared before and after rehabilitation, the children who had rehabilitated were found to have higher reading, spelling, sentence comprehension and mathematical calculation skills with statistical significance. After the rehabilitation of 106 students, found that a mean score of I.Q increasing from 85.43 to 90.11 mean score with statistical significance. After rehabilitation, the children were found to have higher mean scores. Furthermore, in asking the children about knowledge on self-protection from toxins in the environment, most of the children (64.2%) were found to have low knowledge about self-protection from arsenic. After participation in environmental awareness skill promotion activities, most of the sample (41.9%) was found to have higher knowledge on self-protection from toxins at a medium level. Furthermore, the project disseminated research findings and expanded effects for society on a broad scale with announcements of news, research findings and conclusions of preliminary research findings for 15 government agencies and the societal sector including to short documentary for published online in order to push work at the policy and social levels, which will lead to monitoring, prevention, problem-solving, rehabilitation of intellectual skills and learning in children, thereby giving children awareness about self-care and protection, which will solve problems with sustainability. This project funded by the Health System Research Institute (HSRI).


